스프링의 기본 예외 처리 방법
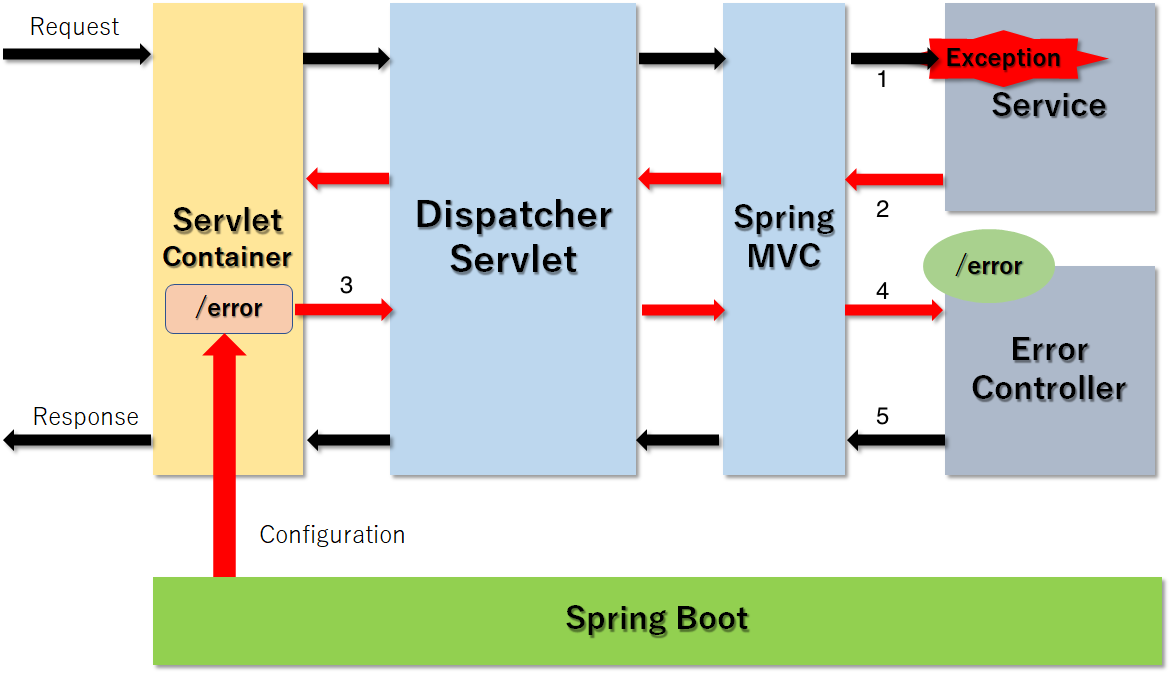
자바 프로그램은 예외가 발생하면 예외 정보를 남기고 스레드가 종료되는 반면에 스프링은 예외가 발생했을 때 웹 애플리케이션이 종료되지 않고 HTTP 상태 코드가 노출이 됩니다. 스프링 부트는 컨트롤러 이하에서 발생한 예외를 캐치하여 스레드를 종료 시키는 것이 아닌 예외 내용을 디스패처서블릿에서 에러컨트롤러로 다시 요청을 보냄으로써 마치 정상 요청인 것처럼 예외 내용을 처리하도록 동작하게 됩니다. 하지만 최초 요청과 더불어 예외 요청을 위해 컨트롤러를 2번 호출한다는 것은 꽤나 복잡하다고 느껴지며 또 이는 필터나 인터셉터를 2번 호출하는 것과 같은 다른 문제를 야기할 수 있습니다.
이런 중복 호출을 방지하기 위해 필터는 등록할 때 DispatcherType을 설정 할 수 있으며 별다른 설정이 없다면 DispatcherType이 ERROR일 경우에는 호출되지 않도록 설정 되어 있습니다.
인터셉터는 최초 인터셉터 등록 시 URI 패턴으로 에러 URI나 다양한 URI를 URI 패턴으로 제외할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Configuration
public class SampleConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Value(value="${server.error.path}")
private final String errorPath;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new SampleInterceptor())
.excludePathPatterns(errorPath);
}
}
BasicErrorController
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
...
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
...
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
}
스프링 부트는 기본적으로 예외를 캐치하여 호출할 에러 컨트롤러로 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.BasicErrorController 를 구현해 사용하고 있습니다. 베이직에러컨트롤러는 /error 경로일 때 실행되는 컨트롤러로 이는 properties에서 server.error.path의 값으로 변경 가능합니다. 주요 메소드로는 errorHtml(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse), error(HttpServletRequest)가 있는데, 해당 메소드는 에러컨트롤러를 호출할 때 들어오는 리퀘스트의 유형에 따라 반환하는 타입이 다릅니다.
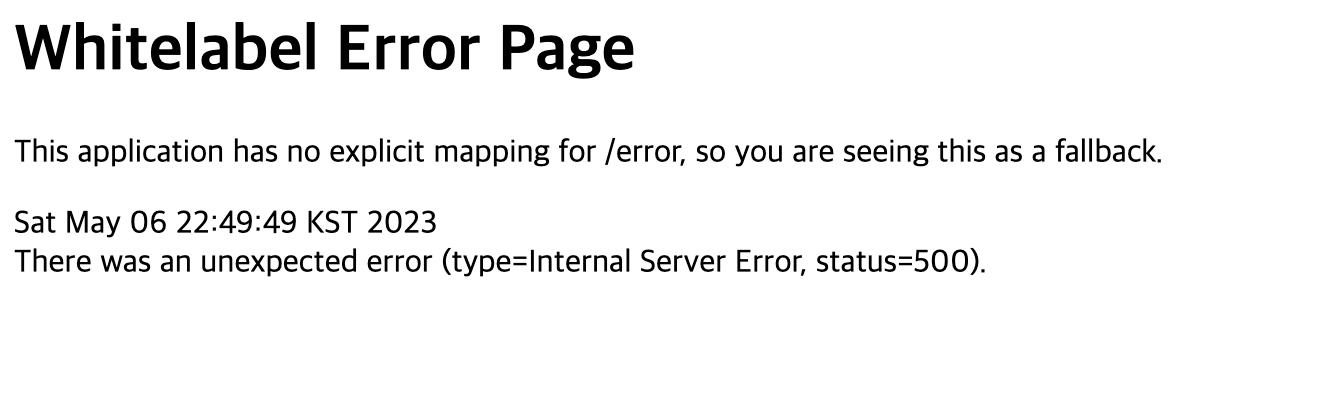
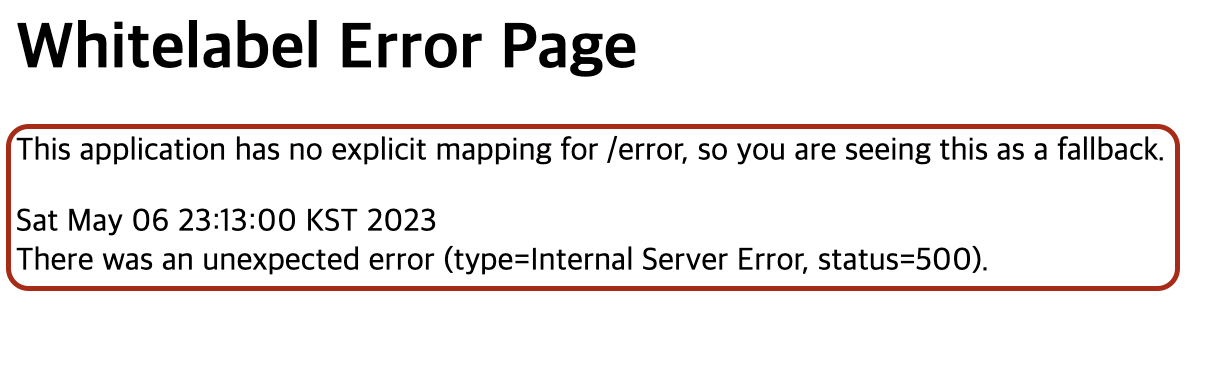
메소드 네임에서 유추할 수 있듯이, errorHtml()같은 경우는 @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) 어노테이션을 적용해, HTTP 요청 헤더의 Accept 값이 text/html일 경우 랜더링하기 위한 ModelAndView 객체를 반환합니다. 따로 에러 페이지를 설정을 하지 않았다면, 기본 에러 페이지인 Whitelabel Error Page 화면이 노출됩니다.
그 외로 경우라면, error() 메소드를 통해 리스폰즈 객체가 반환이 됩니다.
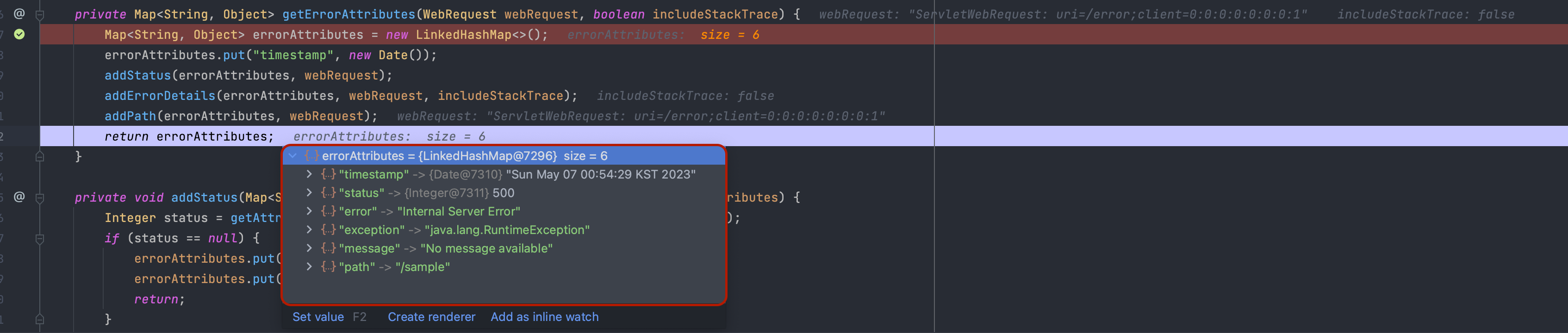
추가로 베이직에러컨트롤러는 예외 처리시 필요한 에러 속성 값을 처리하는데, getErrorAttributes(HttpServletRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions) 메소드를 통해 웹 화면 또는 json으로 보여질 속성 값들을 가져옵니다.
DefaultErrorAttributes에서 제공하는 기본 예외 속성으로 가능한 경우 아래와 같은 속성 값을 제공합니다.
- timestamp: 예외 발생 시간
- status: Http 상태
- error: 에러 코드
- exception: 최상위 예외 클래스 이름(설정한 경우)
- message: 예외 메세지(설정한 경우)
- errors: BindingExecption에 의해 생긴 예외 목록(설정한 경우)
- trace: 에러 스택 트레이스(설정한 경우)
- path: 예외가 발생한 URL 경로
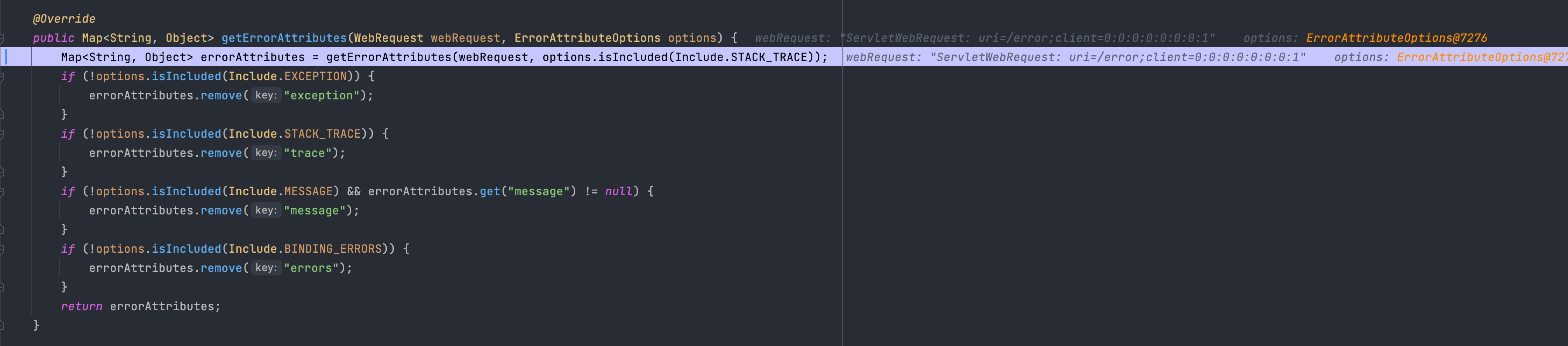
그 후 DefaultErrorAttributes에서는 전체 에서 속성값들 중에서 에러 속성 옵션에 맞게 속성을 설정합니다.
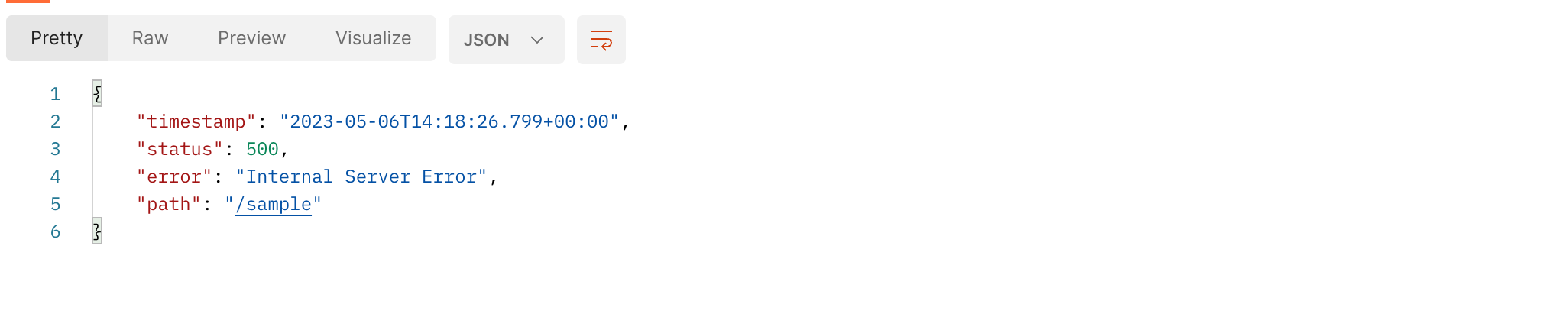
exception, message에 대한 속성 설정 후 결과적으로 아래와 같은 에러 속성을 클라이언트에게 반환합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
"timestamp": "2023-05-06T14:35:44.799+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"path": "/sample"
}
결과적으로 json 객체와 웹 화면에 가각 timestamp , status , error , path에 대한 에러 속성 값들이 바인딩되어 나타납니다.
하지만 위와 같은 응답은 클라이언트 입장에서는 다소 불친절하게 느껴질 수 있습니다. 클라이언트는 Internal Server Error라는 다소 모호한 메시지보다는 명시적으로 해당 오류에 대한 유의미한 응답 메세지를 받고 싶을 것입니다. 그러므로 별도의 다양한 에러 처리를 통해 상황에 맞는 적절한 에러 응답을 제공해야 합니다.
스프링이 제공하는 예외 처리 방법
HandlerExceptionResolver
HandlerExceptionResolver는 컨트롤러 이하에서 발생한 예외를 서블릿 컨테이너까지 전달하지 않고, 스프링 MVC 내부에서 예외 처리를 하기 위해 만들어진 객체입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/**
* Interface to be implemented by objects that can resolve exceptions thrown during
* handler mapping or execution, in the typical case to error views. Implementors are
* typically registered as beans in the application context.
*
* <p>Error views are analogous to JSP error pages but can be used with any kind of
* exception including any checked exception, with potentially fine-grained mappings for
* specific handlers.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 22.11.2003
*/
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
/**
* Try to resolve the given exception that got thrown during handler execution,
* returning a {@link ModelAndView} that represents a specific error page if appropriate.
* <p>The returned {@code ModelAndView} may be {@linkplain ModelAndView#isEmpty() empty}
* to indicate that the exception has been resolved successfully but that no view
* should be rendered, for instance by setting a status code.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the
* time of the exception (for example, if multipart resolution failed)
* @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution
* @return a corresponding {@code ModelAndView} to forward to,
* or {@code null} for default processing in the resolution chain
*/
@Nullable
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex);
}
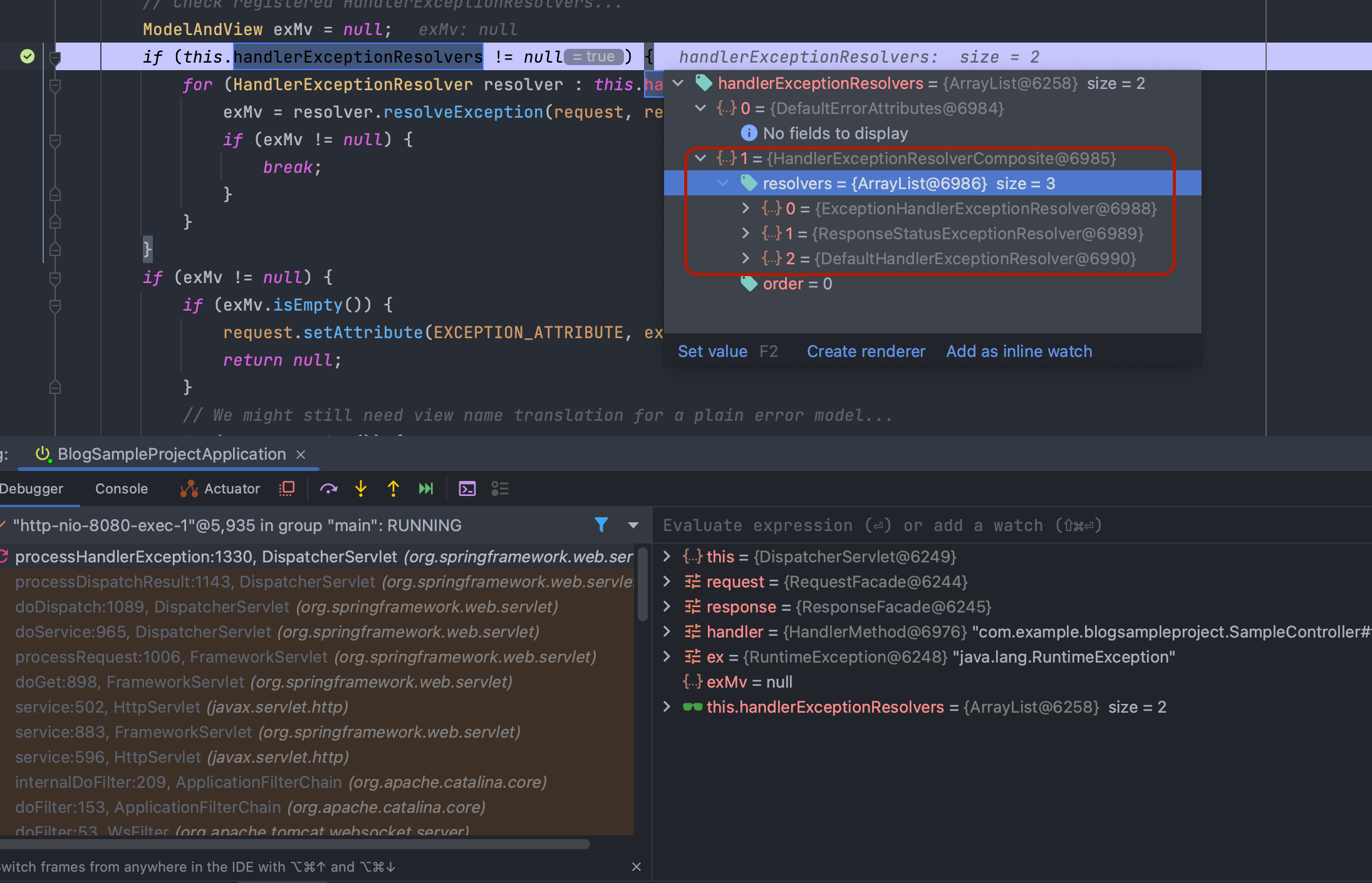
스프링은 예외 처리 로직을 메인 로직으로부터 분리하여 다양한 전략으로 예외를 처리할 수 있도록 추상화할 수 있는 HandlerExceptionResolver 인터페이스를 구현했습니다. 실제로 스프링 부트는 HandlerExceptionResolver를 상속 받아 구현한 다양한 이셉션 처리 로직이 있으며, 해당 객체들은 우선 순위에 따라 처리하게 됩니다.
예외가 발생 했을 때 적용 가능한 구현체를 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite가 담고 있는 목록입니다. 각 구현체들은 아래의 나열된 순서대로 우선 순위를 가집니다.
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver:
@ExceptionHandler를 처리합니다. - ResponseStatusExceptionResolver: HTTP 상태 코드를 지정해줍니다. (
@ResponseStatus,ResponseStatusException를 처리합니다.) DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver: 스프링 내부의 기본 예외들을 처리합니다.
- DefaultErrorAttributes: 에러 속성을 처리하기 위한 객체로, 직접적인 예외를 처리하지않습니다.
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
표준 Spring MVC 예외들을 처리하는 HandlerExceptionResolver 구현체로 발생한 예외들을 적절한 HTTP 상태 코드로 변경해주는 역활을 합니다.
아래 표는 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver에서 변경해주는 예외 HTTP 상태 코드입니다.
| Exception | HTTP 상태 코드 |
|---|---|
| HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException | 405 (SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED) |
| HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException | 415 (SC_UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE) |
| HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException | 406 (SC_NOT_ACCEPTABLE) |
| MissingPathVariableException | 500 (SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) |
| MissingServletRequestParameterException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| ServletRequestBindingException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| ConversionNotSupportedException | 500 (SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) |
| TypeMismatchException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| HttpMessageNotReadableException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| HttpMessageNotWritableException | 500 (SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) |
| MethodArgumentNotValidException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| MissingServletRequestPartException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| BindException | 400 (SC_BAD_REQUEST) |
| NoHandlerFoundException | 404 (SC_NOT_FOUND) |
| AsyncRequestTimeoutException | 503 (SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE) |
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver는 아래의 doResolveException()를 통해 표준 Spring MVC 예외를 위의 표에서 매핑되는 HTTP 상태 코드로 변환합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) {
return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(
(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) {
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported(
(HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) {
return handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable(
(HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException) {
return handleMissingPathVariable(
(MissingPathVariableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) {
return handleMissingServletRequestParameter(
(MissingServletRequestParameterException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException) {
return handleServletRequestBindingException(
(ServletRequestBindingException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException) {
return handleConversionNotSupported(
(ConversionNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException) {
return handleTypeMismatch(
(TypeMismatchException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException) {
return handleHttpMessageNotReadable(
(HttpMessageNotReadableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException) {
return handleHttpMessageNotWritable(
(HttpMessageNotWritableException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
return handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(
(MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException) {
return handleMissingServletRequestPartException(
(MissingServletRequestPartException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof BindException) {
return handleBindException((BindException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException) {
return handleNoHandlerFoundException(
(NoHandlerFoundException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException) {
return handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException(
(AsyncRequestTimeoutException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
}
catch (Exception handlerEx) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", handlerEx);
}
}
return null;
}
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
@ResponseStatus 어노테이션을 사용하여 예외를 HTTP 상태 코드에 매핑하는 HandlerExceptionResolver 구현체로 스프링 v5.0부터는 ResponseStatusException 예외도 함께 처리합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof ResponseStatusException) {
return resolveResponseStatusException((ResponseStatusException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
ResponseStatus status = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(ex.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class);
if (status != null) {
return resolveResponseStatus(status, request, response, handler, ex);
}
if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) {
return doResolveException(request, response, handler, (Exception) ex.getCause());
}
}
catch (Exception resolveEx) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", resolveEx);
}
}
return null;
}
위 코드에서 알 수 있듯이 발생한 예외 클래스가 ResponseStatusException 인스턴스인지 확인하고, AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation() 메소드를 통해 @ResponseStatus 어노테이션으로 마킹된 타겟의 속성값을 찾아 예외 처리합니다. @ResponseStatus 어노테이션같은 경우는 직접 입력해야하기 때문에 라이브러리의 예외 코드 같은 곳에는 작성할 수 없으며, 개발자가 조건에 따라 동적으로 직접 처리해야하는 부분은 ResponseStatusException을 사용하면 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver가 예외 처리를 진행합니다.
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver는 스프링에서 관리되는 ExceptionResolver들 중에서 우선 순위가 가장 높은 객체로, @ExceptionHandler 어노테이션을 처리하기 위한 ExceptionResolver입니다.
먼저 @ExceptionHandler 어노테이션은 예외 클래스들의 속성을 받아 처리할 예외를 지정합니다. 예외 클래스를 지정하지 않는다면, 어노테이션이 선언된 메소드의 인자로 설정한 예외를 처리합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ExceptionHandler {
/**
* Exceptions handled by the annotated method. If empty, will default to any
* exceptions listed in the method argument list.
*/
Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {};
}
@ExceptionHandler는 몇가지 어노테이션과 함께 사용 할 수 있는데, @ResponseStatus를 사용하여 HTTP 상태 코드를 지정할 수 있고 @ResponseBody를 사용하여 반환 타입을 json 형태로 반환 할 수도 있습니다.
다음은 @ExceptionHandler 어노테이션의 사용 예시입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult handleException(Exception e) {
return new ErrorResult(500, e.getMessage());
}
static class ErrorResult {
private int code;
private String message;
public ErrorResult(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
}
@ExceptionHandler은 처리할 예외 클래스를 배열로 지정해 다양한 예외 클래스들을 한 번에 처리할 수 있으며, 지정한 부모 예외 클래스는 자식 예외 클래스도 함께 처리할 수 있습니다.
하지만 자식 예외 클래스 예외 처리 메소드가 구현이 되어 있다면 당연히 자식 예외 클래스가 우선 처리됩니다.
@ExceptionHandler는 위와 같이 다양한 예외 클래스들을 보다 더 깔끔하고 명시적으로 예외처리를 할 수 있도록 도와주지만, 컨트롤러에 구현해야하기 때문에 특정 컨트롤러에서만 발생하는 예외만을 처리할 수 있습니다. 컨트롤러에 정상 로직 코드와 에러 처리 코드가 섞이기 때문에 스프링에서는 전역적으로 예외를 처리할 수 있는 추가적인 기능을 제공합니다.
@ControllerAdvice & @RestControllerAdvice
@ExceptionHandler을 전역적으로 사용하기 위해 스프링 v3.2(@ControllerAdvice), v4.3(@RestControllerAdvice) 부터 지원하게된 어노테이션입니다. 두 개의 어노테이션은 각각 Controller, RestController 처리해주는 점에 있어서 다릅니다.
ControllerAdvice 동작 원리
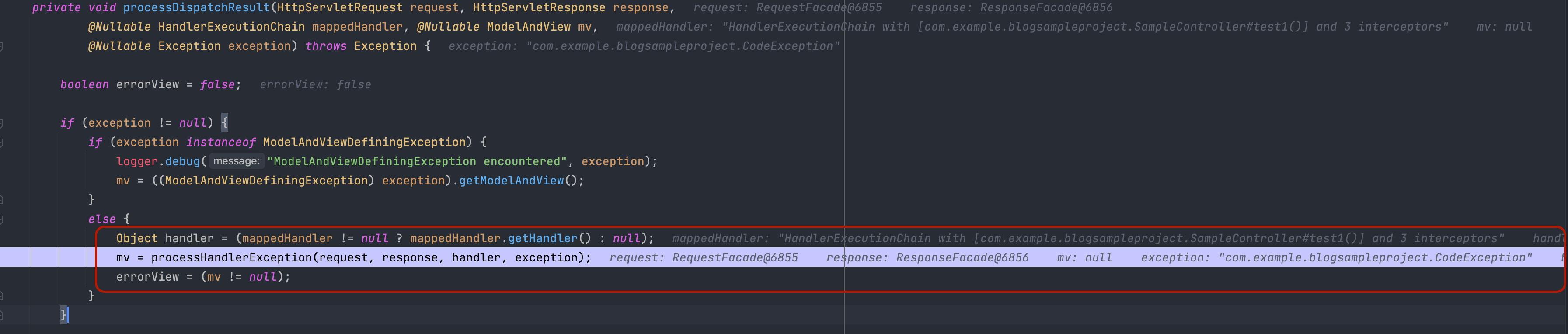
먼저 DispatcherServlet에서 예외를 캐치한 후 예외를 처리하기 위한 메소드가 실행이 됩니다.
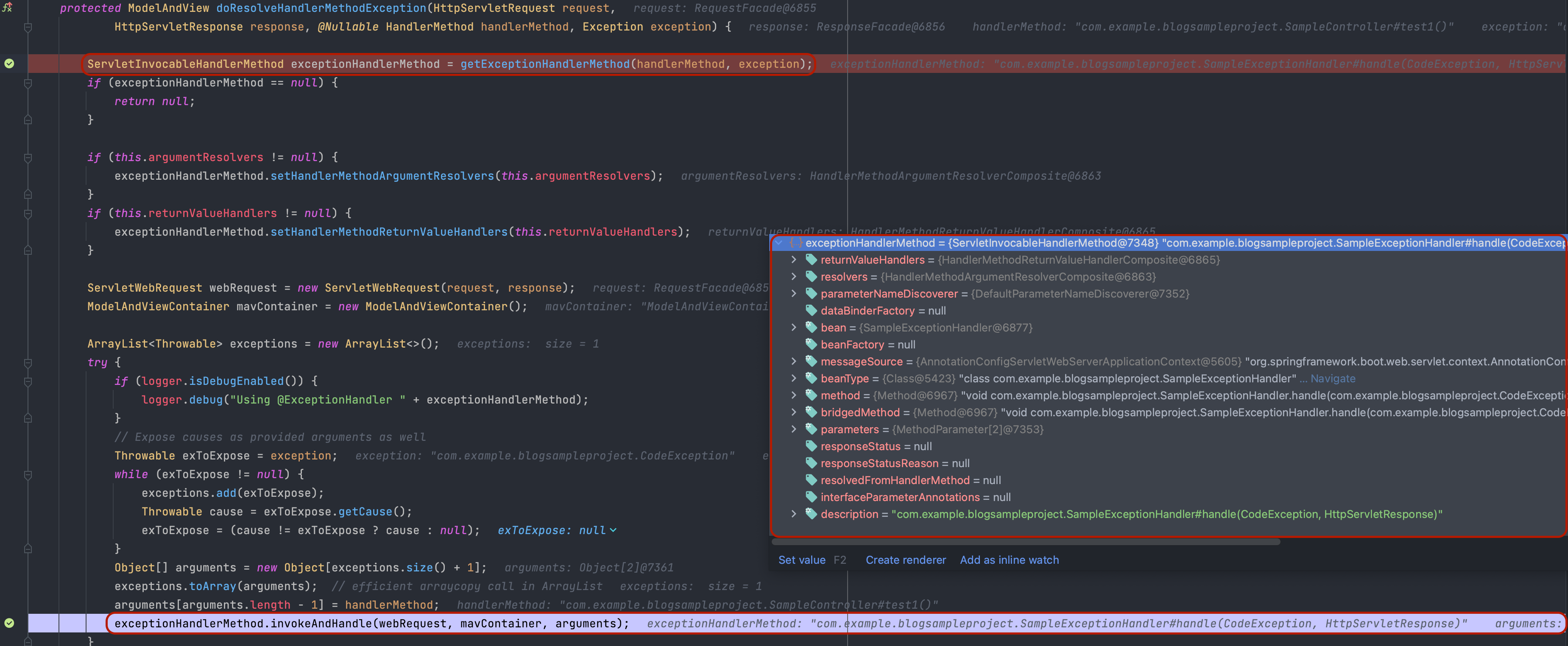
그 후 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver가 해당 예외를 처리하기 위해 위임받으며, 전달 받은 예외에 대한 @ExceptionHandler 메소드를 찾습니다. 기본 설정은 컨트롤러 클래스 계층에서 메소드를 먼저 찾으며, 없는 경우에는 스프링 빈 ControllerAdvice를 찾습니다.
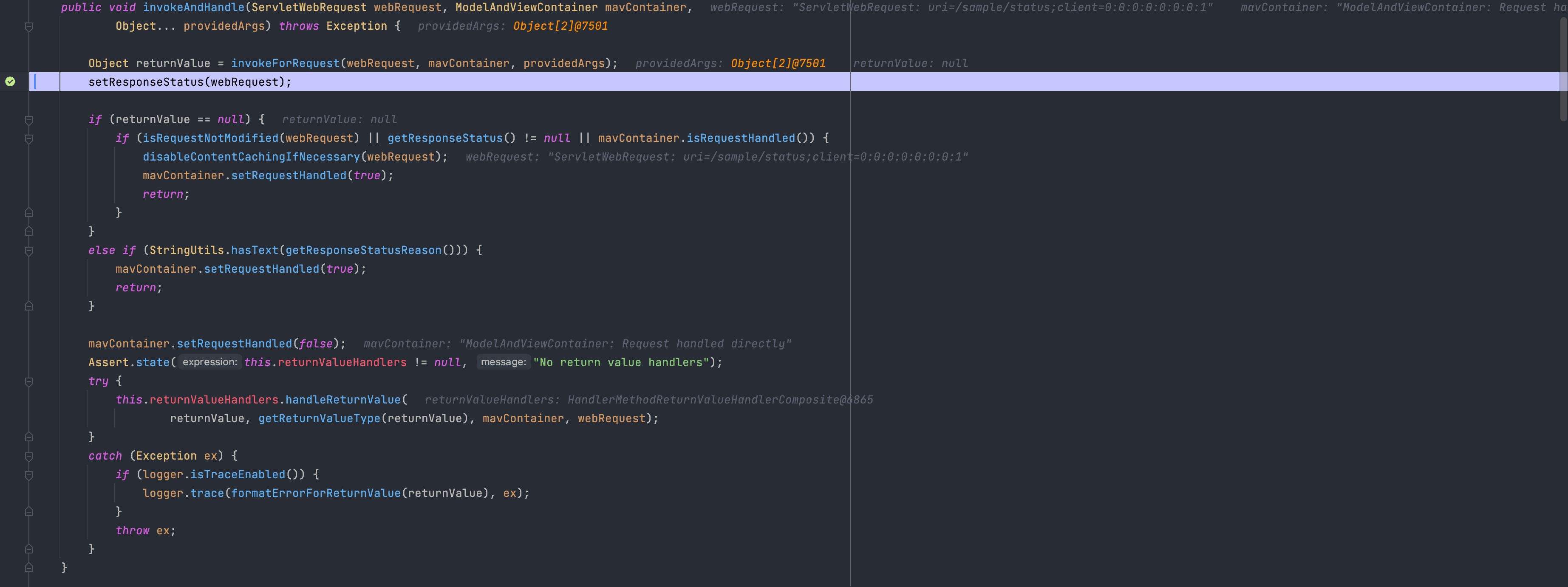
정상적으로 @ExceptionHandler 메소드를 찾았다면, 메소드 실행에 필요한 arguementResolvers, returnValueHandlers... 세팅과 같은 사전 작업을 진행 후 리플랙션을 활용해 메소드를 실행시킵니다.
리스폰즈 설정까지 마친 후 최종으로 설정된 ModelAndView 값에 따라 후속 조치를 한 후 클라이언트의 요청을 종료하고 예외를 반환하게 됩니다.
마지막으로 ControllerAdivce를 사용하는데 있어 주의할 점으로는 아래와 같습니다.
- 특정 예외 클래스를 처리할
ControllerAdvice를 작성할 때는 스프링에서 이미 구현 해놓은ExceptionHandler가 있는지 확인 후 구현해야합니다. 클라이언트에게 일관된 에러 응답을 제공하기 위해 해당ExceptionHandler를 상속 받아 메소드 오버라이딩을 하는 등 후속 처리가 필수입니다. - 여러개의
ControllerAdvice를 구현해놓았다면, basePackages를 설정해 적용 범위를 제한해야합니다. 설정한 basePackages는 해당 패키지와 그 하위에 있는 컨트롤러가 대상이 됩니다. 또 여러 ControllerAdvice가 있을 때 스프링은@Order나 @Priority어노테이션을 기준으로 정렬되며, 순서를 지정하지 않는다면 스프링은 임의의 순서로 처리할 수 있으므로 주의해야합니다.
@ControllerAdvice & @RestControllerAdvice를 통해 하나의 클래스로 모든 컨터롤러의 예외 처리를 전역적으로 수행할 수 있게 됐으며, 컨트롤러 클래스는 메인 로직과 관련된 코드만이 존재하게 됩니다. 관심사 분리를 통해 각각의 클래스에는 각자의 관심사에만 집중할 수 있으며, 이는 관리가 용이해지고 코드의 가독성을 향상시킴으로써 이점을 얻을 수 있게 됐습니다.
오탈자 및 오류 내용을 댓글 또는 메일로 알려주시면, 검토 후 조치하겠습니다.